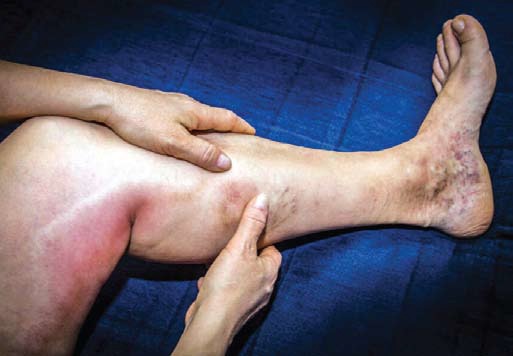
This is a serious condition in which blood clot forms in a deep vein inside your body. A blood clot is a clump of blood that is turned into a solid state. Deep vein blood clot typically forms in your thigh or lower leg, but they can also develop in other areas of your body.
Other names associated with this condition may include, -Thombo embolism, Post thrombotic syndrome, Postphlebitic syndrome DVT symptoms.
According to the center for disease control (CDC), symptoms of DVT only occur in about half of the people with this condition; these include, Swelling in your foot, ankle or leg usually on one side.
-Clamping pain in your affected leg that usually begins in your calf.
-Severe, unexplained pain in your foot or ankle, an area of skin that feels warmer than the skin in the surrounding areas.
The skin over the affected area turning pale or reddish or bluish color, depending on the skin tone of people with extremity DVT or blood clot in the arm may not experience symptoms, if they do, common symptoms are;
-Neck pain, shoulder pain, swelling in the arm or hand, weakness in the hand. People may not find out they have DVT until they have under gone emergency treatment for a pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung) A pulmonary embolism can happen when a DVT clot have moved from the arm or leg into the lung. When an artery in the lung becomes blocked, its life threatening and requires emergency care.
CAUSES AND RISK FACTORS.
DVT is caused by blood clot. The clot blocks a vein preventing blood from properly circulating in your body.
INJURY. Damage to a blood vessel’s wall can narrow or block blood flow; Blood clot may form as well.
SURGERY. Blood vessels can be damaged during surgery, leading to the development of a blood clot. Bed rest with little or no movement after surgery may also increase your risk of developing a blood clot.
REDUCED MOBILITY OR INACTIVITY When you sit frequently, such as during a long flight, blood can collect in your legs, especially the lower parts. If you cannot move for extended periods, the blood flow in your legs can slow down, this can cause clot to form.
CERTAIN MEDICATIONS. Some medications increase the chances of your blood clotting. These include birth control pills, hormone therapy drugs, steroids and antidepressants.
AGE. DVT can still happen in any age, but the incidence in older ages increases. Only 1 in 10000 people younger than 20 get DVT, but among those older than age 80, its 1 in 100.
TRAUMA. Having an injury that damages your veins, like a bone fracture, can cause blood clot to develop.
OBESITY Being overweight can put more pressure on your legs and pelvic veins.
PREGNANCY. This increases the risk of DVT; in fact pregnant people are 5-10 times more likely to develop DVT than those who are not pregnant.
FAMILY HISTORY. Having relatives who have had DVT you likely to develop DVT.
CANCER. Having pancreatic, lung, stomach or brain cancer as well as other cancers puts you at risk of getting DVT especially if you are undergoing chemotherapy. Other health conditions can increase the risk for DVT include; -Covid – 19, tuberculosis, Diabetes, Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
COMPLICATIONS. Major complication of DVT is pulmonary embolism. You can develop a pulmonary embolism if a blood clot moves to your lungs and blocks blood vessel. This causes a serious damage to your lungs and other parts of your body. Get immediate medical help if you have signs of a pulmonary embolism which includes; Dizziness, Sweating, Chest pain that gets worse with coughing or inhaling deeply, Rapid breathing, Rapid heart rate.
TREATMENT. DVT is a serious medical condition. Tell your doctor immediately if you think you’re experiencing symptoms of DVT or go to the closest emergency room where a health care professional can check out your symptoms. DVT treatments focus on keeping the clot from growing. In addition, treatment may help prevent a pulmonary embolism and lower your risk of having more clots. Your doctor may prescribe medications to thin your blood. These blood thinning medications make it harder for your blood to clot. If you don’t work or the DVT is severe, you might use the thrombolytic drugs which work by breaking up the clots. You will receive these through the vein.
HOME REMEDIES. Once a DVT clot is diagnosed, your doctor prescribe medication to help thin the blood or break up the clot, you can combine the above with;
INCREASED MOVEMENT. If possible, take daily walks to improve blood flow, shorter frequent walks are better than one long walk.
KEEP YOU R LEG OR ARM ELEVATED. This is especially important for the legs. Blood can pool if your feet are on the ground all day. Use a stool or a chair to keep your feet elevated and close to the level with your hips.
EAT HEALTHFULLY. Eating a nutrient-dense and balanced diet is important for helping to avoid life threatening complications. Diet high in fibers, fruits and vegetables may be the best for people at risk of DVT. Vitamins like K can bypass warfarin’s ability to thin your blood and prevent a clot.
PREVENTION.
-A healthy life style incorporates many necessary changes to prevent blood clots from forming. These include moving more, quitting smoking and maintaining a moderate weight.
-Managing your blood pressure, Getting out of your car during a long drive and stretch at regular intervals. Walking in the aisles if you’re flying or taking a train, Stretch your legs and feet while you’re sitting. This keeps your blood moving steadily in your calves. Don’t wear tight clothes that can restrict blood flow.
This article is written by Dr. Matovu Richard and Sponsored by SDI